 Department of Conservation and Recreation
Department of Conservation and Recreation
Conserve. Protect. Enjoy.
 Department of Conservation and Recreation
Department of Conservation and Recreation
 Table of Contents
Table of ContentsNorthern Hardwood Forests
Vegetation of this group consists of mixed hardwood forests occurring at high elevations (> 900 m [3,000 ft]) in western Virginia. Southern Appalachian examples range from the high elevations of North Carolina and Tennessee to southwestern Virginia and eastern Kentucky. Central Appalachian examples range from southwestern Virginia northward to the high Allegheny Mountains and the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau of northern Pennsylvania and southern New York.
Northern Hardwood Forest communities have distinct regional variation and floristic composition at a given site varies with geography and specific site conditions. Southern Appalachian Northern Hardwood Forests are prevalent throughout the high-elevation Mount Rogers-Whitetop Mountain (Balsam Mountains) area of the Southern Blue Ridge (Grayson, Smyth, and Washington Counties), with more local outliers at the highest elevations of the Iron Mountains (Grayson and Smyth Counties), Clinch Mountain (Russell, Smyth, Tazewell, and Washington Counties), and Black Mountain (Wise County) on the Kentucky border. Co-dominant trees in Southern Appalachian stands are sugar maple (Acer saccharum, American beech (Fagus grandifolia), yellow birch (Betula alleghaniensis), and yellow buckeye (Aesculus flava) in variable proportions. Fraser magnolia (Magnolia fraseri), eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis), and red spruce (Picea rubens) are important associate trees in some stands, particularly in the Mount Rogers - Whitetop area. Sapling sugar maple, striped maple (Acer pensylvanicum) and mountain maple (Acer spicatum) are common understory species. Smooth blackberry (Rubus canadensis) and hobblebush (Viburnum lantanoides) are common shrubs. Herb layers are moderately sparse to moderately dense, with graminoid-rich patches tending to occur on the drier slope convexities. Some of the most abundant herbs in the Southern Appalachian Northern Hardwood Forests are Appalachian white snakeroot (Ageratina altissima var. roanensis), southern lady fern (Athyrium asplenioides), evergreen wood fern (Dryopteris intermedia), mountain wood aster (Eurybia chlorolepis), sweet white violet (Viola blanda), and Appalachian woodland sedge (Carex austrolucorum).

Northern Hardwood stands in the Central Appalachians occur extensively at high elevations (>900 m [3,000 ft]) of Allegheny Mountain in Highland County, with smaller-patch outliers occurring on north-facing slopes over 1,070 m (3,500 ft) in the Blue Ridge, Ridge and Valley, and Cumberland Mountains, south to Tazewell, Russell, and Wise Counties. These are dominated by sugar maple, black cherry (Prunus serotina var. serotina), yellow birch, northern red oak (Quercus rubra), red maple (Acer rubrum), and sweet birch (Betula lenta var. lenta), while American beech, and eastern hemlock are less frequent co-dominants. Overstory composition varies occasionally to nearly pure sugar maple. Striped maple, mountain maple, and mountain holly (Ilex montana) are the chief understory species, along with sapling sugar maple and beech. The herb layers of many stands are characterized by patch-dominance of hayscented fern (Dennstaedtia punctilobula). Other more or less characteristic herbaceous species include whorled wood aster (Oclemena acuminata), evergreen wood fern (Dryopteris intermedia), prickly tree-clubmoss (Dendrolycopodium dendroideum, stiff clubmoss (Spinulum annotinum), tall millet grass (Milium effusum var. cisatlanticum), grove bluegrass (Poa alsodes), northern shorthusk (Brachyelytrum aristosum), purple oat grass (Schizachne purpurascens), sedges (particularly Carex appalachica, Carex flexuosa, Carex digitalis, Carex leptonervia, and Carex woodii), eastern rose mandarin (Streptopus lanceolatus), and sweet white violet (Viola blanda). The importance of red maple, sweet birch, northern red oak, and black cherry in contemporary Central Appalachian examples of this community group reflects secondary succession following catastrophic logging and fire disturbances in the early part of the twentieth century. Sugar maple and beech, both abundant in understory layers and locally co-dominant in the overstory, appear positioned to assume dominance as current secondary stands mature. However, beech-bark disease and excessive deer browsing are serious threats to the future viability of the largest stands on Allegheny Mountain .
In Virginia, several northern songbirds, including the brown creeper (Certhia americana), mourning warbler (Oporornis philadelphia), and yellow-bellied sapsucker (Sphyrapicus varius), breed only in northern hardwood forests.
References: Adams et. al . (2003), Coulling and Rawinski (1999), Fleming and Coulling (2001), Fleming and Moorhead (1996), Rawinski et al . (1996), Rheinhardt and Ware (1984).
Click here for more photos of this ecological community group.
 © DCR-DNH, Gary P. Fleming.
© DCR-DNH, Gary P. Fleming.
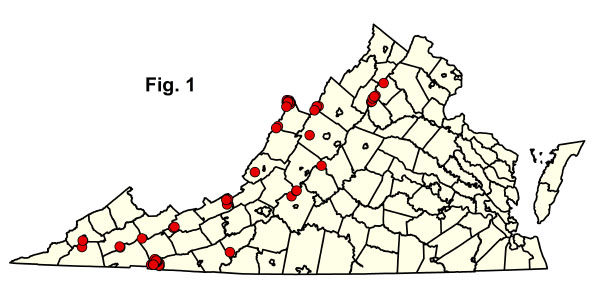
Northern hardwood forests have been well sampled in Virginia , especially in the Mount Rogers-Whitetop area of the Southern Blue Ridge and on Allegheny Mountain in Highland County. To date, 79 plots of this group have been sampled in 18 counties (Fig. 1), although some of the classified units are better supported by plot data than others. However, additional sampling is not likely to change the basic concepts of these units. Click on any highlighted CEGL code below to view the global USNVC description provided by NatureServe Explorer.
 Download a spreadsheet of compositional summary statistics for each of the community types listed below.
Download a spreadsheet of compositional summary statistics for each of the community types listed below.